Choosing the right allergy eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis depends on the type and severity of your symptoms. Some drops help relieve itching, while others target redness, swelling, or dryness. Identifying what’s causing your eye irritation—such as pollen, pet dander, or dust—can point you to the best eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis and improve how well the treatment works.
At Penn Medicine Becker ENT & Allergy, our team offers clear, helpful guidance to support safe and effective treatments so you can feel better and protect your eye health.

What is Allergic Conjunctivitis?
Allergic conjunctivitis occurs when the thin membrane that covers the white part of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids, also known as the conjunctiva, becomes inflamed. This inflammation is caused by a reaction to common allergens such as tree pollens, pet dander, dust mites, or mold. When the eyes come into contact with these allergens, the immune system reacts, causing the release of histamine and other chemicals that lead to symptoms of eye allergies. For more information, you can review our specific page on allergic conjunctivitis and available treatment options—or contact us directly to speak with a member of our team.
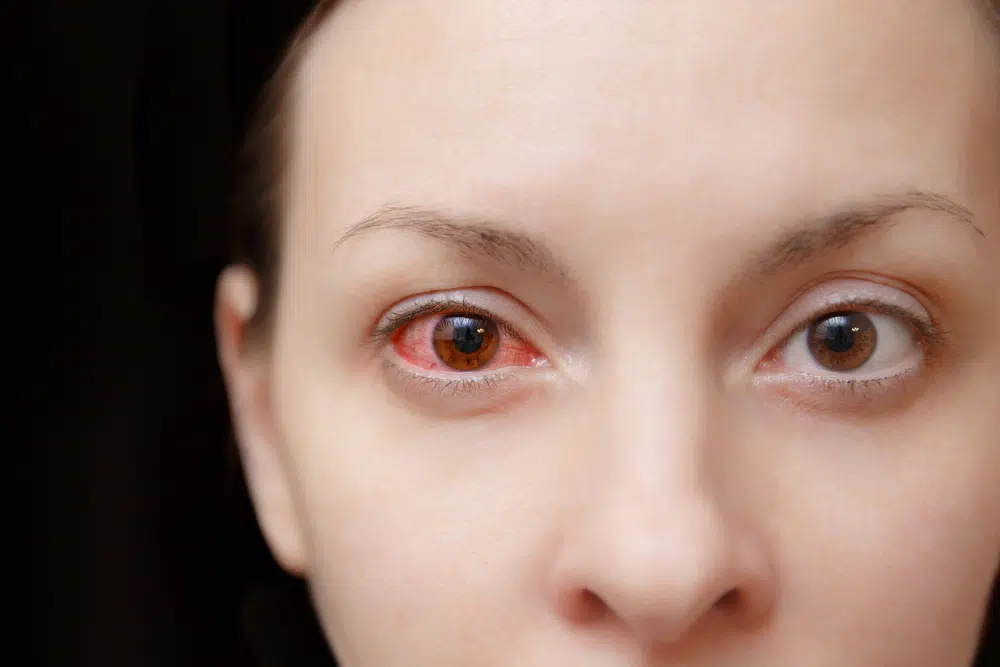
Symptoms of Allergic Conjunctivitis
The most common symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis include:
These symptoms can be accompanied by other allergy symptoms such as sneezing, runny or itchy nose, and sore throat.
Why Eye Drops are Effective in Treating Allergic Conjunctivitis
Eye drops can target the specific symptoms of the condition. They can help to reduce inflammation, itching, and redness while also providing relief from other allergy symptoms. Additionally, eye drops can be applied directly to the affected area, offering quick and targeted relief. An allergy expert at Penn Medicine Becker ENT & Allergy can help you determine the most effective eye drop option for allergic conjunctivitis.
6 Types of Eye Drops Available for Allergic Conjunctivitis
Several types of eye drops are available to treat allergic conjunctivitis, each with its own benefits and potential side effects. It’s important to choose the right type of eye drop based on your specific symptoms.
1. Antihistamine Drops
Antihistamine eye drops work by blocking the release of histamine, a chemical released during the allergic response that causes itching, redness, and swelling. These drops, such as Alaway Antihistamine Eye Drops, can provide quick relief from eye allergy symptoms and are typically available over the counter or by prescription.
2. Mast Cell Stabilizer Drops
Although not an antihistamine, mast cell stabilizers, like olopatadine hydrochloride, also prevent the release of histamine and other chemicals from mast cells, which are involved in the allergic response. These drops can help prevent symptoms from occurring, especially during pollen season, and are often used in combination with antihistamine eye drops for more effective relief. Mast cell stabilizer eye drops are typically available by prescription.
3. Combination Drops
Combination eye drops contain both an antihistamine and a mast cell stabilizer, offering the benefits of both types of drops in one product. These prescription drops can be effective for treating both short-term symptoms and providing long-term relief from allergic conjunctivitis.
4. Decongestant Drops
Decongestant eye drops, like naphazoline hydrochloride, help to reduce redness and swelling in the eyes by constricting the blood vessels in the conjunctiva. These drops can temporarily relieve allergic conjunctivitis symptoms but are not recommended for long-term use due to potential side effects, such as rebound redness and increased eye pressure. Decongestant drops are typically available over-the-counter.
5. Prescription Drops
Prescription eye drops may include more potent antihistamines, mast cell stabilizers, or corticosteroid eyedrops. These drops are prescribed by a healthcare professional and are usually reserved for more severe cases of allergic conjunctivitis or when over-the-counter options have not provided sufficient relief.
6. Over-the-Counter Drops
Over-the-counter antihistamine or decongestant drops for allergies can be used to provide relief from mild to moderate symptoms. However, it is important to carefully read and follow the instructions on the label, and seek medical attention if symptoms do not improve or worsen.
Additionally, artificial tears, such as Systane Ultra Lubricant Eye Drops, can help relieve dry eye symptoms that often accompany allergic conjunctivitis. These drops work by mimicking natural tears, providing moisture and lubrication to the eyes.
Choosing the Right Eye Drops for Allergic Conjunctivitis
Selecting the most effective eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis depends on understanding your symptoms and the underlying causes of your allergies. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed choice:
- For Immediate Itch Relief: If your primary concern is quick relief from itching, antihistamine eye drops (e.g., Alaway Antihistamine Eye Drops) are designed to block the action of histamines, providing fast relief from itchy, watery eyes.
- For Long-Term Management: If you’re looking for a solution to prevent allergic reactions before they start, especially during allergy season, mast cell stabilizer drops (e.g., olopatadine hydrochloride) can be effective. These drops prevent the release of histamines and other chemicals from mast cells, reducing the likelihood of an allergic reaction.
- For Severe Allergies: For individuals with severe allergies that don’t respond well to other treatments, combination drops that include both an antihistamine and a mast cell stabilizer offer dual-action relief and may be more effective.
- For Redness and Swelling: Decongestant eye drops (e.g., naphazoline hydrochloride) can reduce redness and swelling in the eyes by constricting blood vessels. However, they are generally recommended for short-term use only due to potential side effects.
- Consulting a Healthcare Professional: It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as an allergist or ophthalmologist, who can recommend the best type of eye drop based on your specific symptoms and medical history. They can also advise on the proper usage and any precautions to take when using these medications.
Find Relief from Allergic Conjunctivitis with Personalized Care
Tired of itchy, red eyes? Our allergy specialists can help you find the right eye drops fast.
How to Properly Use Eye Drops for Allergic Conjunctivitis
It is essential to use eye drops for allergic conjunctivitis correctly to ensure they are effective. Always wash your hands before following these general steps for proper application:
- Tilt your head back and gently pull down your lower eyelid to create a small pocket.
- Hold the eye drop bottle or dropper above the eye, being careful not to touch the eye or eyelid with the tip.
- Squeeze the bottle or dropper to release the recommended number of drops into the eye.
- Close your eye gently and press the inner corner of the eye for about 30 seconds to prevent the drops from draining into the tear duct.

The Possible Side Effects of Using Eye Drops for Allergic Conjunctivitis
Choosing the right eye drops for relief from allergic conjunctivitis is crucial, but it’s equally important to be aware of potential side effects. This knowledge ensures you’re fully informed about what to expect, helping you make the best decision for your health. Below, we explore the side effects associated with different types of eye drops used in treating allergic conjunctivitis.
Antihistamine Eye Drops
These may include mild burning or irritation upon application, dry eyes, and blurred vision. Typically, these symptoms are temporary and should diminish as your eyes adjust to the treatment.
Mast Cell Stabilizer Eye Drops
Users might experience a brief stinging or burning sensation, possible headaches, or discomfort in the eyes. With consistent use as directed, these side effects often reduce over time.
Combination Eye Drops (Antihistamine and Mast Cell Stabilizer)
Expect similar side effects to both antihistamine and mast cell stabilizers, such as temporary irritation, dryness, or a mild burning sensation. The combination formula aims to minimize the need for multiple medications, potentially reducing the overall side effect profile.
Decongestant Eye Drops
These can include rebound redness with prolonged use, dilated pupils, and increased eye pressure in susceptible individuals. It’s advisable to use these drops sparingly and not for extended periods.
Prescription Eye Drops
There’s an increased risk of glaucoma, cataracts, and eye infections with long-term use of certain prescription eye drops. These should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional who can monitor for these risks.
When to See a Doctor for Allergic Conjunctivitis
While eye drops can be effective in managing allergic conjunctivitis symptoms, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional if:
- Symptoms do not improve after using over-the-counter eye drops for several days.
- Symptoms become more severe.
- There is significant pain, eye discharge, or changes in vision.
- You suspect a bacterial or viral infection, as these require different treatments.

