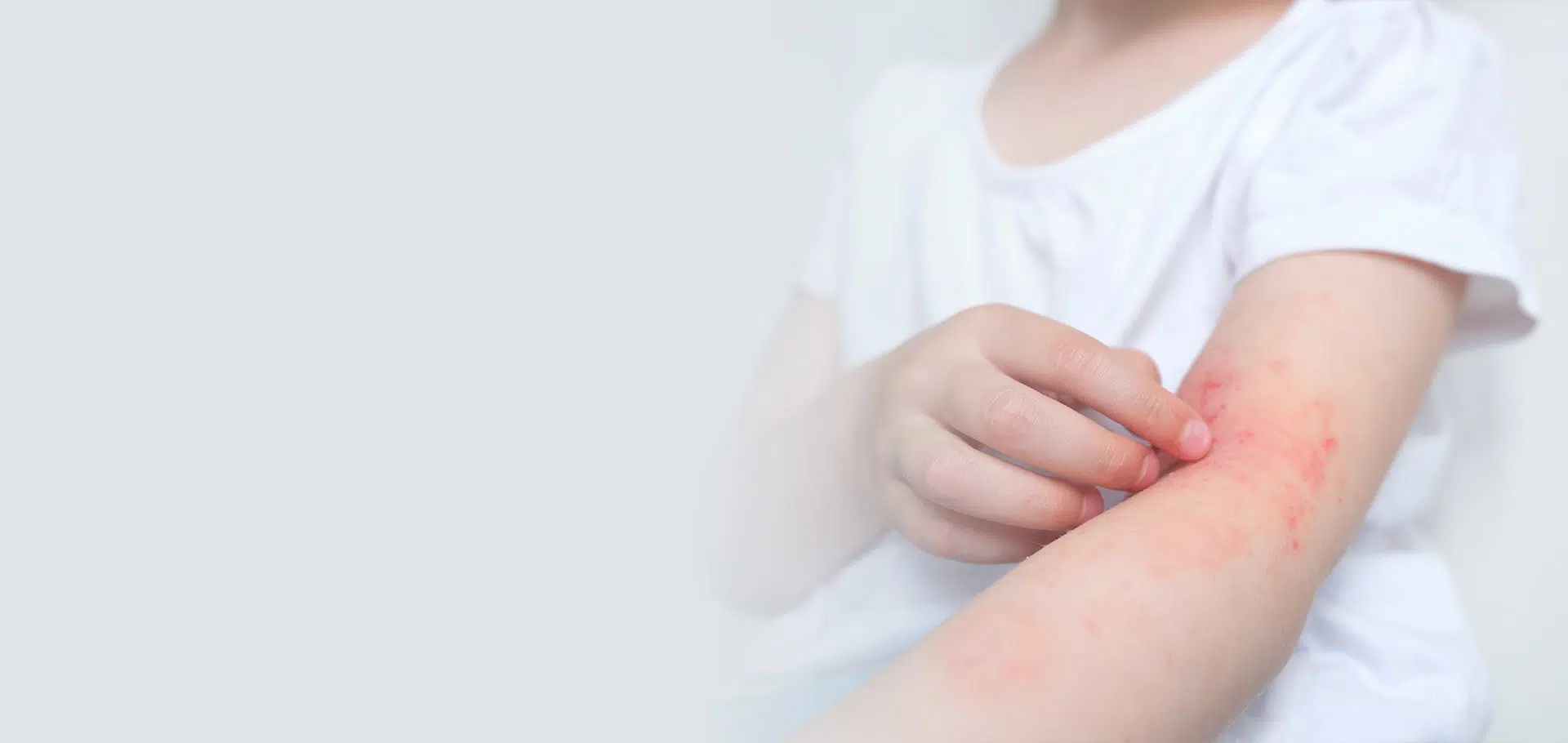
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Allergic contact dermatitis is a common skin condition that occurs when the skin comes into contact with a substance that causes an allergic reaction, making the skin uncomfortable and unsightly.
- What is Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
- What Causes Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
- Types of Skin Reactions Caused by Allergic Contact Dermatitis
- What specific symptoms can be observed in individuals experiencing Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
- Preventative Measures for Avoiding Allergic Contact Dermatitis
- Treatment Options for Allergic Contact Dermatitis
- Frequently Asked Questions about Allergic Contact Dermatitis
What is Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis is an inflammatory skin condition triggered by an allergic reaction to certain substances that come into contact with the skin. Common allergens include cosmetics, detergents, plants, metals, and other environmental factors. Atopic dermatitis is a separate condition from allergic contact dermatitis but may have similar symptoms and can be confused with it.
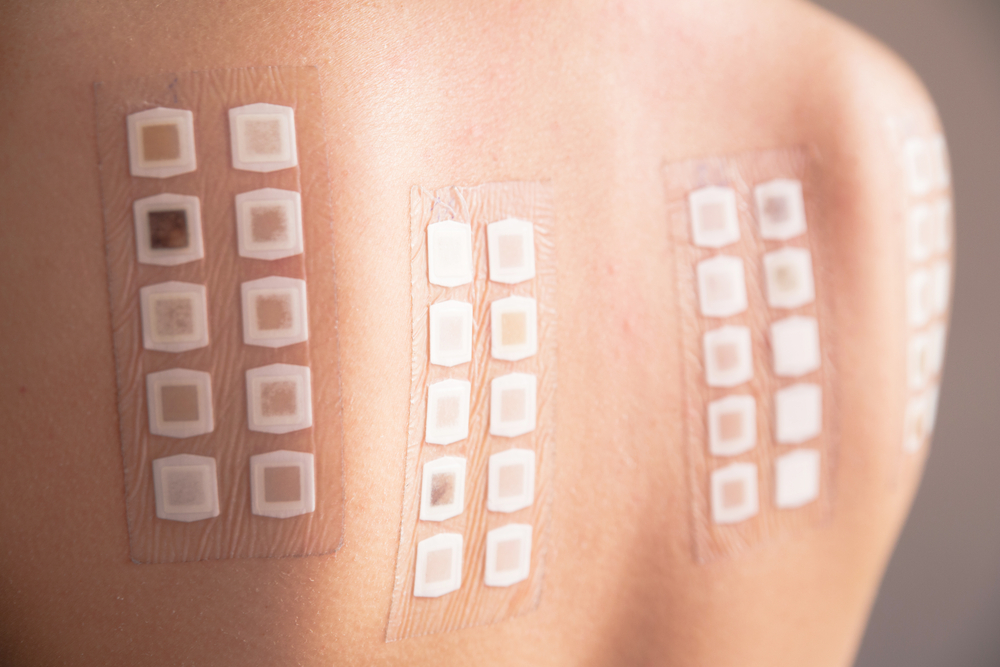
Depending on the severity of the reaction, treatment may include topical antibiotics, immunosuppressive agents, or hydrocortisone cream to reduce inflammation. If there is suspicion of an allergy to a particular substance or material, patch testing may be performed to isolate the exact cause of the allergic reaction. Barrier creams are also available to protect sensitive areas from coming into contact with potential allergens as well as scaly skin irritation.
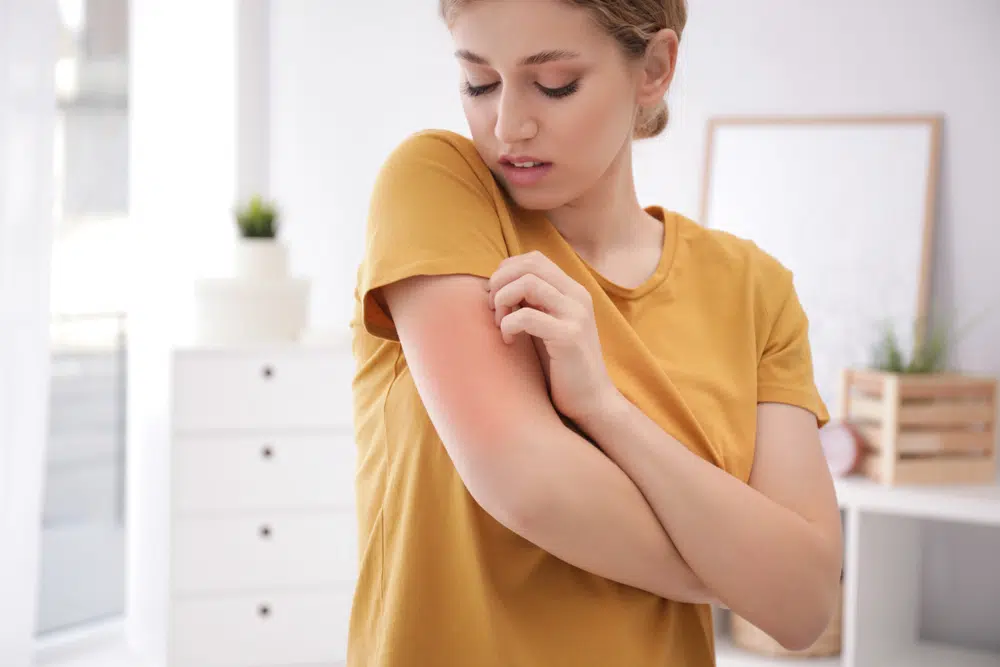

In more severe cases of allergic contact dermatitis, further tests such as skin biopsies may be needed in order to confirm the diagnosis and rule out any other underlying conditions. With proper medical care and management, most cases can be managed effectively, and patients can often avoid future exposure or reactions.
What Causes Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
Allergic contact dermatitis is the immune system’s response to a specific allergen. In some cases, the cause of contact dermatitis may be difficult to identify, especially if the reaction is delayed or if multiple substances are involved.
Allergens in the Environment
Common environmental allergens that can cause allergic contact dermatitis include pollen, mold spores, and animal dander.
Contact with Chemicals and Metals
Exposure to certain chemicals and metals, such as cleaning products or nickel, can lead to an allergic reaction. Nickel is commonly found in jewelry, belt buckles, and other metal objects that come into contact with the skin.
Exposure to Plant Resins and Pollens
Some plants, such as poison ivy, poison oak, and pine, produce resins that can cause an allergic reaction. Many people also react to ragweed or grass pollen. A variety of tree pollens can also be problematic for some people.
Allergic Reaction to Cosmetics, Toiletries, and Detergents
Many personal care products, including cosmetics, toiletries, and detergents, contain ingredients that can cause an allergic reaction. Common culprits include fragrances, hair dye, rubber gloves, and certain preservatives.
Prolonged Exposure to Sunlight
Some people are predisposed to sun sensitivity. Others develop allergy symptoms only after being triggered by another factor, such as taking medication or coming into contact with certain plants.
Types of Skin Reactions Caused by Allergic Contact Dermatitis
We are familiar with the various types of skin reactions caused by allergic contact dermatitis. Chronic dermatitis is a long-lasting form of contact dermatitis that can be caused by either direct or indirect contact with certain substances, such as nickel-containing jewelry or even acrylic nails. Photoallergic contact dermatitis is a type of hypersensitivity reaction that occurs when the outer layer of human skin is exposed to ultraviolet light and then comes into direct contact with an irritating substance. Photocontact dermatitis is similar to photoallergic contact dermatitis, but instead of ultraviolet light being the triggering factor, it is usually the direct contact with a specific allergen that causes the reaction.
During a physical examination, an allergist may observe linear streaks on the skin or swelling around regional lymph nodes. Depending on the severity of symptoms, treatment may include topical immunomodulatory agents or corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and itching. In more severe cases, definitive treatment may involve avoiding any further exposure to the allergen or the use of systemic medications such as antihistamines or leukotriene receptor antagonists.
For recurrent cases of allergic contact dermatitis, it is important to identify and avoid any potential triggers in order to prevent future episodes. Acute cases should be treated promptly with appropriate medical care in order to minimize discomfort and irritation in affected areas. By taking proactive steps and avoiding known allergens, most people can successfully manage their allergic response and enjoy healthy skin for many years to come.
What specific symptoms can be observed in individuals experiencing Allergic Contact Dermatitis?
The severity of the reaction can vary depending on the individual’s sensitivity to the allergen, the amount of exposure, and the duration of exposure.
Itchy Red Skin
Allergic contact dermatitis typically causes the skin to itch. Lighter skin can turn red, while darker skin can turn dark brown, purple, or grey.
Burning and Stinging Sensation
In addition to itching, some people may experience a burning or stinging sensation at the site of the reaction.
Blistering and Rashes
In more severe cases, allergic contact dermatitis can cause blisters and an itchy rash on the skin.
Dry, Flaky, or Cracked Skin
As the skin becomes inflamed and irritated, it may become dry, flaky, or cracked, making it more vulnerable to infections or other skin conditions.
Swelling and Pain
In some cases, the affected area may become swollen and painful, particularly if the reaction is severe or the skin has been repeatedly exposed to the allergen.
Preventative Measures for Avoiding Allergic Contact Dermatitis
While it can be challenging to completely avoid all allergens, there are some preventative measures that can help reduce the risk of developing allergic contact dermatitis:
- Identifying and avoiding known allergens
- Using hypoallergenic personal care products
- Wearing gloves when handling potential irritants, such as cleaning products or certain metals
- Washing hands thoroughly after coming into contact with potential allergens
- Applying a barrier cream to protect the skin from potential irritants
If you suspect you have allergic contact dermatitis, the allergist physicians at Penn Medicine Becker ENT & Allergy in New Jersey and Philadelphia can help you identify the cause and provide the appropriate treatment. Sometimes we will also work with our colleagues in Dermatology.
Schedule your consultation
Treatment Options for Allergic Contact Dermatitis
The choice of treatment for allergic contact dermatitis depends on the severity of the reaction, the location of the affected skin, and the individual’s medical history and preferences.
Avoidance of Allergens
The most effective treatment for allergic contact dermatitis is identifying and avoiding the known allergen causing the flare-up. This may involve making changes to personal care products, clothing, or work materials.
Topical Corticosteroid Creams and Ointments
Topical corticosteroids are often prescribed to help reduce inflammation, itching, and redness associated with allergic contact dermatitis. These creams and ointments should be applied to the affected areas as directed by a healthcare provider for the best results.
Oral Antihistamines
Oral antihistamines can help relieve an itchy skin rash and other allergy symptoms associated with allergic contact dermatitis. They work by blocking the action of histamine, a chemical released by the immune system during an allergic reaction.
Ultraviolet Light Therapy
In some cases, ultraviolet (UV) light therapy may be recommended to help calm the skin by suppressing the immune response. This treatment involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of UV light under medical supervision.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy is another treatment option that uses specific wavelengths of light to help reduce inflammation and improve the appearance of the skin. This treatment is typically reserved for more severe cases of allergic contact dermatitis that have not responded to other treatments and is often combined with other treatments.
Immunosuppressant Medications
In severe cases of allergic contact dermatitis, immunosuppressant medications may be prescribed to help suppress the immune system’s response to the allergen. These medications should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider and may have potential side effects.
Allergy Shots
Allergy shots, also known as allergen immunotherapy, may be recommended for patients with severe allergic contact dermatitis that have not responded to other treatments. This treatment involves injecting small amounts of the allergen into the body to help the immune system build tolerance over time. Allergy shots may help reduce the severity of allergic reactions and the need for medications.

Pick one of our convenient locations
for your Allergic Contact Dermatitis Treatment
