Are your eyes itchy, red, and watering? If so, you might be suffering from allergic conjunctivitis. Because allergic conjunctivitis is closely tied to environmental allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pet dander, allergy specialists at Becker ENT and Allergy are well-positioned to help identify triggers and manage related eye symptoms.
Choosing the right allergic conjunctivitis eye drops can seem overwhelming with all the options available. Let’s ease your journey through this maze, helping you identify the symptoms and provide insight on both over-the-counter and prescription eye drops.

Finding the Best Allergy Eye Drops for Relief
- Allergic conjunctivitis causes itchy, red, and watery eyes, and different eye drops target specific symptoms.
- Antihistamine eye drops help relieve itching and swelling by blocking allergy triggers.
- Artificial tear drops flush out allergens and soothe dry, irritated eyes without medication.
- Over-the-counter eye drops provide quick relief, but prescription options may be necessary for severe allergies.
- Long-term use of decongestant eye drops can lead to rebound redness, so they should be used sparingly.
The Different Types of Eye Allergies
Eye allergies—also known as ocular allergies—can affect people in very different ways. Factors like genetics, environment, and individual sensitivity to allergens all play a role. While some experience only mild, occasional irritation, others may deal with more persistent and severe symptoms.
Seasonal Allergic Conjunctivitis (SAC)
- Most common type
- Triggered by pollen during spring, summer, or fall
- Symptoms include itching, redness, tearing, and swelling
Perennial Allergic Conjunctivitis (PAC)
- Occurs year-round
- Caused by indoor allergens like dust mites, pet dander, and mold
- Symptoms are milder but persistent
Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis (VKC)
- A more serious, chronic form seen mostly in young males
- More common in warm, dry climates
- Can affect the cornea and may lead to vision problems if untreated
Atopic Keratoconjunctivitis (AKC)
- A long-term condition linked with eczema or atopic dermatitis
- Affects mostly adults
- Can cause thickening of the eyelids, scarring, and vision issues
Contact Allergic Conjunctivitis
- Reaction to eye drops, makeup, or contact lens solutions
- Symptoms improve once the irritant is removed
Giant Papillary Conjunctivitis (GPC)
- Often related to wearing contact lenses
- Causes large bumps under the eyelids, itching, and lens discomfort
Find The Best Eye Allergy Drops for You
Choosing the Right Allergy Eye Drops for Allergic Conjunctivitis
Allergy eye drops are a practical solution for providing relief from eye allergy symptoms. These symptoms are often triggered by allergens like pollen, dust mites, and pets, resulting in allergic conjunctivitis. When these allergens come into contact with your eyes, your body responds by releasing histamine and other substances. This reaction leads to common symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis, which can be a sign of pollen allergy symptoms.
Allergy eye drops contain medications that can either block the release of histamine or reduce the inflammation in the eyes. By doing so, they bring significant relief from the discomfort and inconvenience caused by allergic conjunctivitis. For contact lens wearers, it is important to note that allergy eye drops should not be used while wearing the lenses, as this can alter their vision and cause irritation.
It’s important to understand that not all allergy eye drops are the same. Some provide rapid but temporary relief, while others are designed for long-term use. Knowing which types of eye drops to use and when is crucial for effectively managing your eye allergy symptoms.
Antihistamine Eye Drops
Use these if your eyes feel itchy, red, or swollen.
Antihistamine drops are great for fast relief from allergy symptoms caused by histamine—a chemical your body releases when it reacts to allergens like pollen or pet dander.
When they work best:
- For quick relief during allergy flare-ups
- If you have mild to moderate symptoms
- Great for sudden exposure to allergens (like being outdoors on a high pollen day)
- Best antihistamine for swollen eyes
Good to know:
These drops work quickly but might need to be used more than once a day. They’re great for short-term use and safe when used as directed. Oral antihistamines can also help but may cause side effects like drowsiness.
Artificial Tear Drops
Use these if your eyes feel dry, irritated, or gritty.
Artificial tears help flush out allergens from your eyes and keep them moist. They don’t treat the allergy itself, but they do help relieve discomfort.
When they work best:
- As a daily eye care routine
- As a supportive treatment alongside medicated drops
- For contact lens wearers (just remove your lenses before using)
- For people with mild seasonal allergies
Good to know:
Look for preservative-free versions if you use them often. They’re safe for long-term use and can be used with other allergy treatments.
Find the right eye drops to relieve your allergic conjunctivitis symptoms
Book an appointment with our Allergist specialists at Becker ENT and Allergy.
Decongestant Drops
Use these if your main issue is red eyes.
Decongestant drops shrink the blood vessels in your eyes, which helps reduce redness. They work fast but are only meant for very short-term use.

When they work best:
- For occasional redness relief
- Before a special event or photo
- Not recommended for people with glaucoma or certain eye conditions
Good to know:
Avoid using them for more than 2–3 days in a row. Using them too often can actually make redness worse (called rebound redness). Always read the label or talk to your doctor if you’re unsure.
Mast Cell Stabilizer Eye Drops
Use these if you get eye allergy symptoms regularly.
Mast cell stabilizers don’t work instantly but help prevent symptoms if you use them consistently. They stop your body from releasing histamine in the first place.

When they work best:
- For people with chronic or severe allergies
- As a preventive treatment before allergy season
- Best when started a week or two before allergy season begins
Good to know:
These drops are safe for long-term use and often recommended for people who need daily relief. Just be patient—they take a few days to start working.
There’s also a comparison to consider when discussing mast cell stabilizers and oral antihistamines. Oral antihistamines provide quick relief, but they have side effects, such as drowsiness. Meanwhile, mast cell stabilizers may take longer to act, but when administered consistently, they provide a more targeted and sustainable response. Consulting an eye care specialist can help determine the best approach for your condition.
Combination Eye Drops (Antihistamine + Mast Cell Stabilizer)
Use these if you want both quick relief and long-term control.
Combination drops give you the best of both worlds—they relieve symptoms quickly like antihistamines and help prevent future flare-ups like mast cell stabilizers.

When they work best:
- For people who want a single, all-in-one treatment
- If your allergy symptoms are moderate to severe
- Helpful if you’ve tried single-ingredient drops with limited results
Good to know:
These may cost more than single-ingredient drops, but many people find them more convenient. Always check with your provider to make sure they’re a good fit for you.
Things to Keep in Mind When Choosing Eye Allergy Drops
See a specialist: An allergist can help you choose the right type based on your symptoms.
Don’t use drops with contacts in: Always remove your lenses first unless the product is labeled safe for use with contacts.
Stick with the schedule: Some drops work best when used regularly, not just when symptoms appear.
Watch for preservatives: If you need frequent use, preservative-free drops are gentler on your eyes.
How to Apply Eye Drops: A Step-by-Step Guide
Applying eye drops correctly can maximize the medication’s effectiveness and comfort. Follow these steps to ensure you’re getting the most out of your treatment for allergic conjunctivitis:
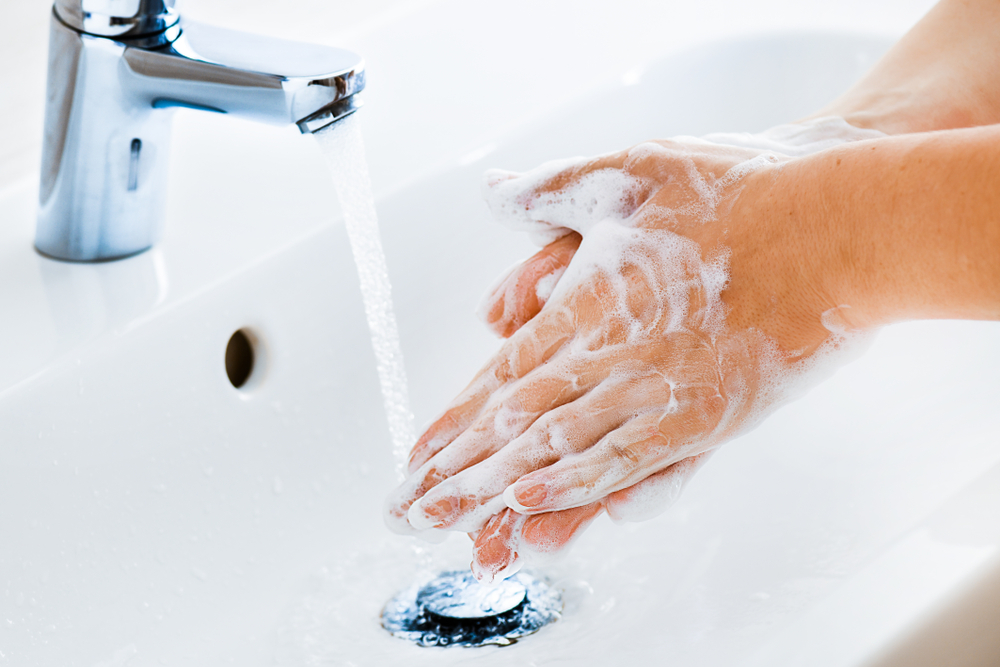

- Wash your hands with soap and water.
- Read the instructions on the eye drop label.
- Shake the bottle if the directions say to.
- Remove contact lenses (unless your doctor says it’s okay to leave them in).
- Open the bottle—be careful not to touch the dropper tip.
Step 1: Prepare
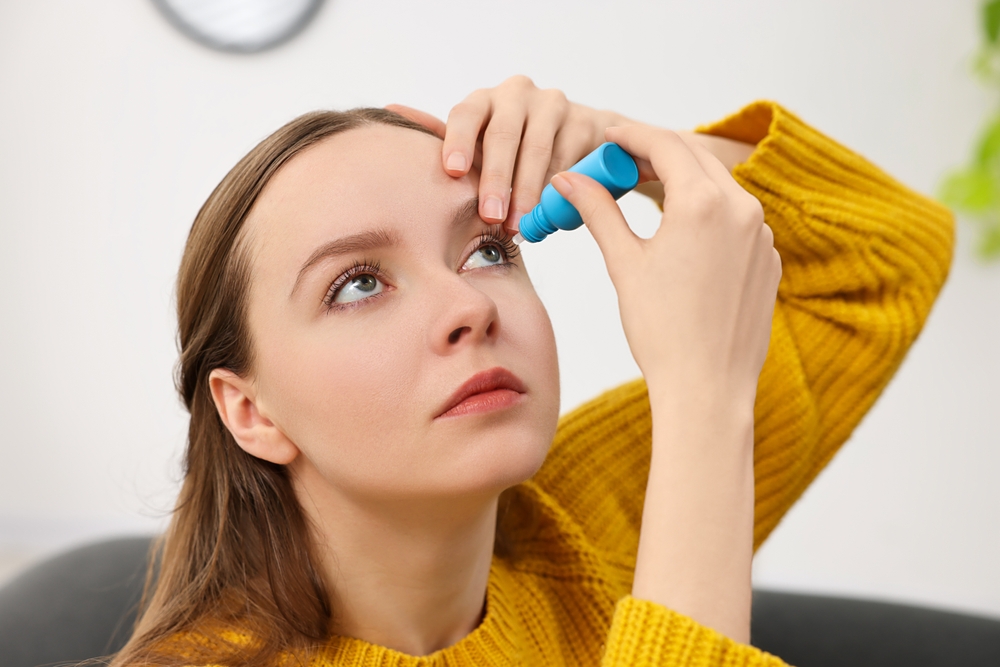

- Tilt your head back and look up.
- Gently pull down your lower eyelid to make a small pocket.
- Hold the bottle above your eye and squeeze one drop into the pocket.
- Don’t let the dropper touch your eye or lashes.
- Close your eye and press the inner corner (near your nose) for about 30 seconds—this helps the drop stay in your eye.
- If you’re using more than one kind of drop, wait 5 minutes between them.
Step 2: Apply the Drops

- Gently blot away any extra drops with a clean tissue.
- Put the cap back on without touching the tip.
- Wash your hands again.
Step 3: Aftercare
Additional Tips
- Avoid blinking vigorously right after applying the drops, as this can increase the likelihood of the medication draining away from the eye.
- Store eye drops as directed. Some may require refrigeration, while others should be kept at room temperature.
- Check the expiration date regularly and discard expired eye drops to avoid irritation or infection.
- Consult your healthcare provider if you experience discomfort, persistent irritation, or if you’re unsure about the correct application method for your eye drops.
Analyzing Over-the-Counter (OTC) vs. Prescription Drops
Over-the-counter eye drops are typically the first line of defense when dealing with allergic conjunctivitis. They can be effective in relieving symptoms, but they may not address the underlying condition.
Moving to prescription medication, they can be Corticosteroid eye drops that contain stronger active ingredients that can significantly reduce inflammation and allergy symptoms. Prescription medications may also include different types of ophthalmic solutions, oral medication, or allergy shots to target specific conditions.
Choosing between an OTC and a prescription product requires understanding the severity, duration, and symptoms of allergic conjunctivitis. For some, an OTC medication is sufficient. But, if your symptoms persist, a prescription-strength product may be required to effectively treat the allergic reaction.
Remember, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting or changing eye drop medication to ensure safe and suitable treatment.
Considerations for Long-Term Use of Eye Drops for Allergic Conjunctivitis
When managing allergic conjunctivitis with eye drops, it’s crucial to understand the implications of long-term use and be aware of potential side effects. Different types of eye drops come with varying recommendations for duration of use, and some may lead to adverse effects if used improperly or for extended periods.
- Decongestant eye drops (e.g., naphazoline, tetrahydrozoline) quickly reduce redness but should not be used for more than 3 consecutive days due to the risk of rebound redness.
- Antihistamine eye drops relieve itching and redness; mast cell stabilizers help prevent symptoms. Some drops combine both for more complete relief.
- These antihistamine/mast cell stabilizer drops are usually safe for longer-term use when used as directed.
- Artificial tears help with dryness and irritation and are safe for long-term use, but preservative-free options are better for frequent use.
- Corticosteroid eye drops are for severe allergic conjunctivitis and require a prescription.
- Long-term corticosteroid use can increase the risk of cataracts, glaucoma, and eye infections, so regular monitoring by an eye care professional is important.
When to Consult a Doctor
In managing allergic conjunctivitis, understanding when to seek professional help is crucial. Certain times may require consultation with a physician, notably when symptoms persist despite taking over-the-counter drugs or using recommended eye drops.
When symptoms intensify or your eyes become unresponsive to prescription medications, it’s a strong indicator to consult a doctor. Ensure you communicate all indications of allergic conjunctivitis to your physician. Ignoring these warning signs may potentially lead to severe complications. Remember, it’s better to be cautious when eye health is at stake.
Talk with an Allergy Specialist
What are the best allergy eye drops? It depends on your specific symptoms, how often they occur, and your overall eye health. Making sense of eye allergy treatments can be challenging on your own. In a topic as critical as eye health, it’s always beneficial to seek expert guidance. Consult with our specialists at Becker ENT and Allergy. They can help interpret your symptoms, advise about potential side effects, and steer you toward an effective, safe solution suitable for your specific needs. Don’t drop the ball on your eye health; book an appointment with us!

