If you’ve ever had sudden swelling in your lips, face, hands, or even your throat — and you weren’t sure why — it might have been something called angioedema. It’s a condition where parts of your body swell up, often because of a reaction to certain foods, medications, or even stress.
Some people are born with it (yep, it can run in families), while others might only experience it because of allergies or certain health issues. No matter the cause, one thing’s for sure: what you eat really matters.
This guide is all about figuring out which foods might trigger those uncomfortable (and sometimes scary) flare-ups, and what safe, delicious options you can enjoy instead. Whether you’re just learning about angioedema or trying to get better at managing it — you’re in the right place.

| Food to Avoid | Why It Triggers Angioedema | Alternatives / Safe Options |
| Tree nuts | Common allergens that cause histamine spikes | Seeds like pumpkin or sunflower seeds |
| Dairy (milk, cheese) | High histamine and casein protein triggers | Lactose-free milk, plant-based yogurts |
| Citrus fruit & berries | Histamine-rich fruits that may worsen swelling | Apples, pears, melons |
| Tomatoes / green salad | Documented triggers in HAE and allergic types | Cooked carrots, cucumbers |
| Fish, shellfish | Common allergens and histamine release | Lean poultry or tofu |
| Spicy foods (chili) | Capsaicin may dilate vessels and trigger swelling | Mild herbs: basil, cilantro |
| Alcohol | Acts as a vasodilator; proven trigger | Hydrating herbal teas, sparkling water |
| Food additives | Preservatives and artificial sweeteners may trigger it | Whole, unprocessed foods |
What Is Angioedema and Why Does It Happen?
Angioedema is a medical condition characterized by deep-seated swelling in the lower layers of the skin and submucosal tissues. Similar to hives, it often affects the face, throat, tongue, hands and feet, but it can also occur in the digestive tract or airways, causing abdominal pain and difficulty in breathing. Angioedema can be triggered by an autoimmune disorder, drug reaction, infection, insect bites, or an allergic reaction to food, medication, or environmental factors. There are several types of angioedema, including acute allergic angioedema, non-allergic drug reaction, idiopathic angioedema, hereditary angioedema, acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency, and vibratory angioedema.
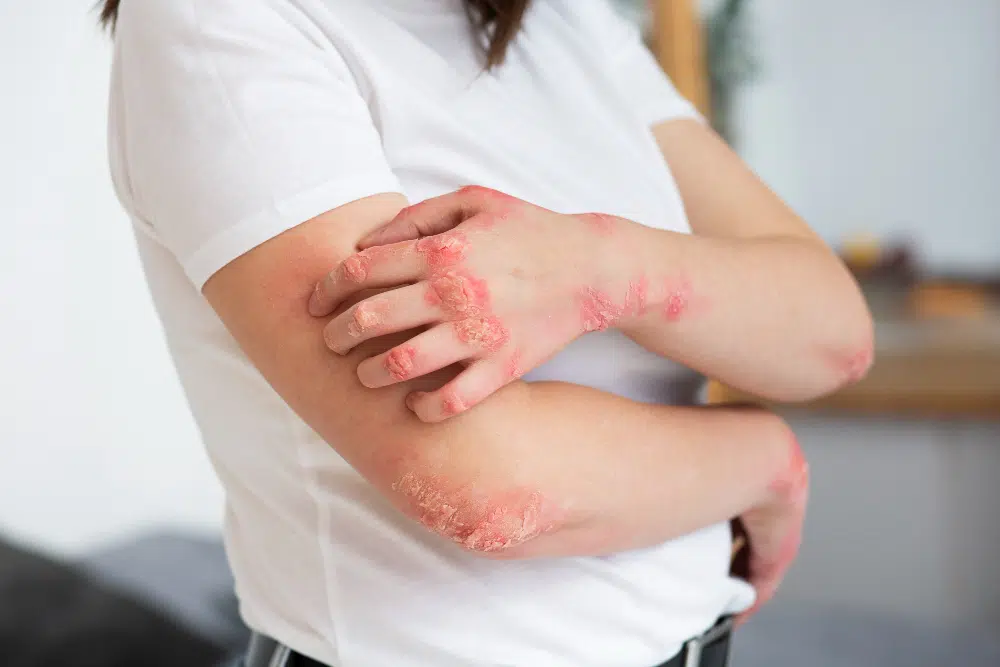

What Are the Different Types of Angioedema?
- Hereditary Angioedema
- Allergic Angioedema
- Idiopathic Angioedema
What Are the Most Common Symptoms of Angioedema?
- Severe swelling in the skin or mucous membranes
- Itching and redness
- Swelling of the lips, eyes, hands, or feet
- Abdominal cramps or stomach pain
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing
- Low blood pressure
Managing Foods that Trigger Angioedema
To effectively manage risk for angioedema and minimize the risk of triggering episodes, it is important to be cautious about the foods you consume. Here are some guidelines to follow:
Understanding Food Allergies and Intolerances
- Differentiating between food allergies and intolerance reaction
- Identifying common food triggers
- Avoiding foods that may cause allergic reactions or intolerances
Which Foods Are Common Triggers for Angioedema?
- Tree Nuts: Be cautious of tree nuts such as almonds, walnuts, and cashews, as they can often trigger angioedema.
- Food Additives: Certain food additives like preservatives and artificial sweeteners may cause allergic reactions in some individuals. Read food labels carefully and avoid products containing these additives.
- Green Salad Ingredients: Some individuals with angioedema may experience swelling after consuming specific green salad ingredients, such as spinach or arugula. Monitor your body’s response and avoid any triggers.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): NSAIDs like aspirin or ibuprofen can cause severe symptoms in individuals prone to angioedema. Consult your healthcare provider for alternative pain management options.
- Spicy Foods: Spices like chili peppers or hot sauces can trigger angioedema in certain individuals. Reduce spice levels in your meals or avoid them altogether.
- Alcohol: Some individuals may experience angioedema episodes after consuming alcohol. Monitor your body’s response and consider avoiding alcohol if it triggers symptoms.
What Are Some Safe and Enjoyable Foods for People With Angioedema?
- Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: Opt for fresh fruits and vegetables that are not known triggers for angioedema. Examples include apples, pears, carrots, and cucumbers.
- Lean Proteins: Choose lean proteins like chicken, fish, and tofu as they are less likely to cause allergic reactions or trigger angioedema.
- Whole Grains: Incorporate whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, and oats into your diet for a nutritious and safe option.
- Hydration: Ensure you stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day. Proper hydration can help reduce the risk of angioedema episodes.
When Should You Talk to a Specialist About Angioedema?
- Consult with an allergist or immunologist: A healthcare professional specializing in allergies and immune system disorders can provide personalized advice and guidance for managing angioedema.
- Keep a food diary: Maintain a record of your food intake and any symptoms experienced. This can help identify specific triggers and guide your conversations with healthcare professionals.
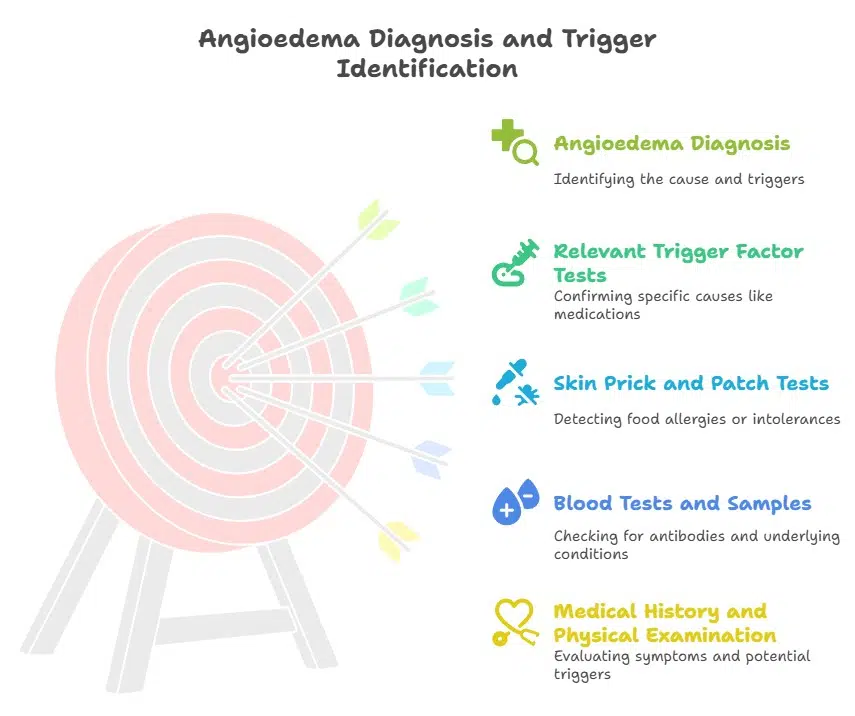
How Do Doctors Diagnose Angioedema and Its Triggers?
To determine the cause of angioedema and identify trigger factors, several diagnostic methods can be employed.
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your medical history and a thorough physical examination will help your healthcare provider evaluate your symptoms and identify potential triggers.
Blood Tests and Samples
Blood tests may be conducted to check for specific antibodies or complement levels. Additionally, taking blood samples can help identify any underlying conditions that may contribute to angioedema.
Skin Prick and Patch Tests
These tests involve applying small amounts of allergens to the skin and monitoring for any reaction. They can help identify food allergies or food intolerance reactions that may trigger angioedema.
Relevant Trigger Factor Tests
If a specific trigger factor is suspected, such as certain medications or food additives, specific tests may be performed to confirm the cause.
Frequently Asked Questions
Contact us!
Managing angioedema requires caution and attentiveness to the foods we consume. By understanding the different types of angioedema, identifying trigger factors, and making informed food choices, individuals can minimize the risk of angioedema episodes. Consulting with healthcare professionals, keeping a food diary, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle is essential for effectively managing this condition. Remember, eating with caution is key to enjoying a healthier life while managing angioedema.

