Lingual tonsil infection, also known as lingual tonsillitis, is a common condition that can affect both adults and children. These infections occur in the lingual tonsils, in the lymphoid tissue located near the back of the tongue.
In some cases, the infection can also lead to more serious complications, such as obstructive sleep apnea or airway obstruction. Lingual tonsillitis is most often the result of a viral infection, but fungal or bacterial tonsillitis can also occur.
What are Lingual Tonsil Infections?
Lingual tonsil infection is a type of throat infection that affects the lingual tonsils, which are one of the four types of tonsils. These tonsils are a part of the body’s lymphoid tissue and are located at the base of the tongue. Lingual tonsillitis can be caused by various factors, including bacterial, viral, and fungal infections. Recurrent infections can lead to other complications.
Causes of Lingual Tonsil Infections

Infected tonsils are primarily caused by exposure to various types of viruses and bacteria. Some factors include:
- Viral tonsillitis is often a result of common viruses such as the Epstein-Barr virus, the influenza virus, and the herpes simplex virus.
- The group A streptococcus bacterium (strep throat), in particular, frequently causes bacterial infections that result in tonsillitis.
- In some cases, the condition can also be triggered by fungal infections. The lingual tonsils, as lymphoid tissue, are part of the immune system and situated at the tongue’s base. They play a crucial role in defending the body against infections. However, when the immune responses are overwhelmed by exposure to viruses, bacteria, or other foreign bodies, the lingual tonsils can become infected, leading to swollen tonsils, a common symptom of tonsillitis.
Recurrent infections can lead to chronic tonsillitis, a condition that may require medical treatment. In some instances, the infection can also result in complications such as airway obstruction, which can exacerbate conditions like obstructive sleep apnea. Other typical symptoms of tonsillitis include a sore throat, bad breath, ear pain, and swollen lymph nodes.
Symptoms of Lingual Tonsil Infections
Lingual tonsil infection can present a range of symptoms that may vary from person to person, including:
- A sore throat is often accompanied by swollen tonsils. These swollen tonsils can be painful or feel like a lump in the throat, causing difficulty swallowing and talking.
- Bad breath can be a sign of a bacterial or viral infection in the lingual tonsils.
- Acute tonsillitis can also cause ear pain and swollen lymph nodes, which can be detected during a physical examination.
In cases of chronic tonsillitis, symptoms may persist over a longer period and may cause recurrent infections of the throat, which can include the palatine tonsils. Chronic pharyngitis, a condition characterized by persistent inflammation of the throat, can also be a sign of chronic lingual tonsillitis.
Diagnosis of Lingual Tonsil Infections
A physical examination is usually sufficient for a diagnosis, but in some cases, further tests may be necessary. Diagnosis of lingual tonsil infections typically involves a thorough ear, nose, and throat examination and a throat swab to test for the presence of bacteria.
In some cases, a complete blood count may also be conducted to look for signs of infection. If the infection is suspected to be caused by a virus, additional tests may be necessary to identify the specific virus involved.
How to Treat Lingual Tonsil Infections
If the bottom of your tongue is sore, swollen, or feels weird when you swallow, it might be a lingual tonsil infection. These tonsils live way in the back of your tongue, and yep—they can get infected just like the ones on the sides of your throat.
The good news? It’s treatable. Here’s how doctors usually help you feel better:
Medicine That Helps Kick the Infection
If bacteria are the problem (like strep throat):
Your doctor might give you antibiotics—these are pills or liquids that fight off the bad bacteria. You might get something like amoxicillin. Important: always finish all your antibiotics, even if you feel better halfway through!
If it’s a fungal infection (less common):
Your doctor might give you special anti-fungal medicine. These help clear up yeast-like infections that can sometimes show up in the throat.
If it’s a virus (like a cold or flu): Viruses don’t respond to antibiotics, so in this case, the focus is on helping you feel better while your body fights it off. Lots of rest and comfort care is key here.
For pain and swelling:
You can take regular over-the-counter meds like:
- Ibuprofen (Advil) – helps with pain and swelling
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) – helps bring down fever and pain
Throat sprays and lozenges can also bring some quick relief.
If allergies are behind it:
Sometimes allergies make your lingual tonsils swell up or feel sore. In that case, allergy meds like:
- Antihistamines (like Zyrtec or Claritin)
- Nasal sprays
- Or even allergy shots (for long-term help)
Easy Things You Can Do at Home
Even if you’re taking medicine, there are a few simple things you can do at home to feel better faster:
- Rest – Seriously, don’t push yourself. Your body needs downtime to heal.
- Drink lots of water – Warm tea, broths, or even ice pops can feel great.
- Gargle with salt water – This sounds weird but actually works! It can calm your throat.
- Use a humidifier – Adds moisture to the air so your throat doesn’t dry out.
- Avoid smoke or strong smells – These can make everything feel worse.
What If It Keeps Coming Back? (Surgery Might Be Needed)
Sometimes lingual tonsil infections just won’t quit. Or the tonsils get so swollen they make it hard to swallow, breathe, or even sleep. In those cases, surgery might be the best option.
This surgery is called a lingual tonsillectomy, which just means taking out those inflamed tonsils at the back of your tongue.
Here’s the deal:
- You’ll be asleep during the procedure.
- It’s done in a hospital or surgical center.
- You’ll probably have a sore throat afterward for a week or two.
- Most people feel way better once they’re healed.
It’s not super common, but if your doctor suggests it, it’s because they think it’ll help your quality of life—especially if infections keep coming back or it’s messing with your breathing or sleep.
When Something Else Is Causing It
Sometimes the infection or swelling isn’t just from germs—it could be caused by other things, like:
- Allergies – We already talked about this. Managing your allergies can help shrink your tonsils back to normal size.
- Acid reflux – If stomach acid keeps sneaking up into your throat, it can really irritate the tonsils. Your doctor might suggest:
- Avoiding spicy or acidic foods
- Taking acid blockers (like omeprazole)
- A weak immune system – If you’re always getting sick, your doctor may want to check if something else is going on inside your body.
Fixing the root problem can stop the tonsil issues from coming back again and again.
When to Call a Doctor
Don’t try to tough it out if:
- You can’t swallow or breathe comfortably
- Your throat pain is getting worse, not better
- You’ve had a fever for more than a couple of days
- It feels like something’s stuck in your throat
Seriously—if something feels off, talk to a doctor. Even if it turns out to be nothing major, it’s better to be safe than sorry.
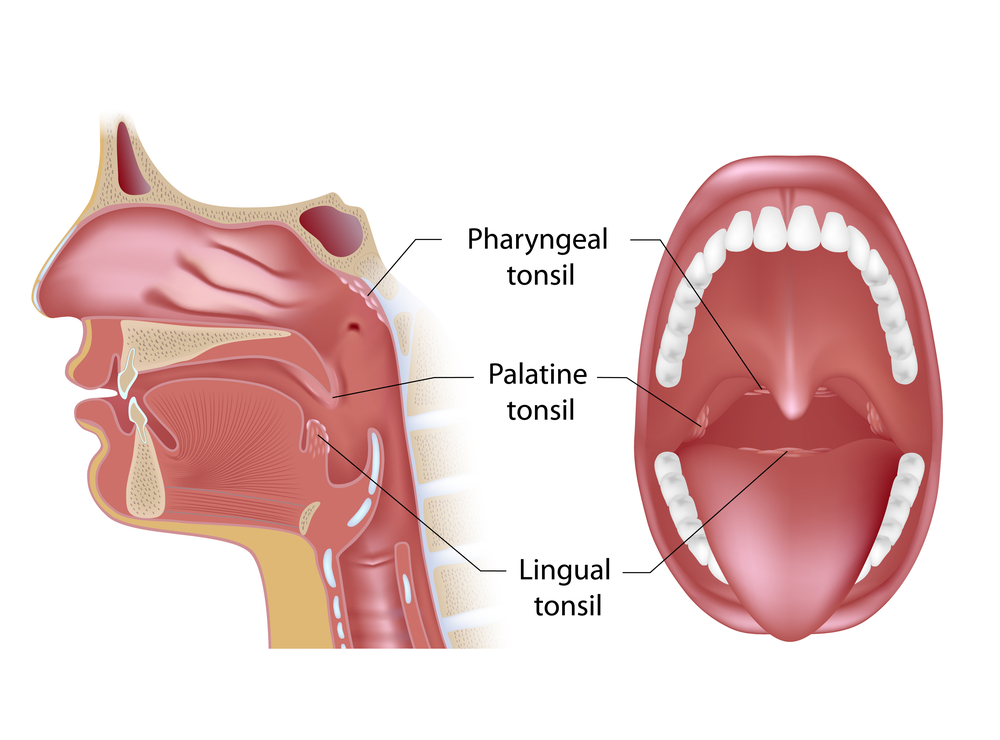
Where Are Lingual Tonsils Located?
Your lingual tonsils are found way in the back of your tongue—at the base, right near where your tongue meets your throat. You can’t usually see them in the mirror like your regular tonsils (the ones on each side of your throat), but they’re still there, doing their job quietly.
Think of them as your body’s little guards. They help catch and fight off germs that come in through your mouth or nose. Even though they’re hidden, they’re an important part of your immune system!ition, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Preventing Lingual Tonsil Infections
Prevention is the best strategy for managing lingual tonsil infections. Some preventive measures include wearing masks in high-risk areas, avoiding contact with infected individuals, and not sharing food or drinks with others who may be infected.
Vaccination against relevant viruses can also be an effective preventive strategy. Regular hand washing and maintaining good oral hygiene are essential to limit the spread of viruses and bacteria that can cause tonsillitis.
Complications Associated with Untreated Lingual Tonsil Infections
Lingual tonsil infections, if left untreated, can lead to a variety of dangerous complications. One common complication is the development of an abscess in the throat, which is a pocket of pus that forms when the body fights off an infection. This can cause severe pain and difficulty swallowing. Another potential complication is rheumatic fever, a serious condition that can damage the heart, joints, and other tissues.
Untreated lingual tonsil infections can also lead to obstructive sleep apnea, a condition that interrupts breathing during sleep. This can result in daytime fatigue, high blood pressure, and other health problems. In some cases, untreated tonsillitis can also lead to airway obstruction, a potentially life-threatening condition that can cause difficulty breathing.
Secure Your Safe Treatment Experience with PennMedicine
Join our satisfied clients who’ve experienced safe, effective treatments.
The Role of Diet and Nutrition in Managing Tonsillitis
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in managing tonsillitis. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals can boost the immune system and help the body fight off infections.
Certain foods, such as fruits and vegetables and lean proteins, can provide nutrition that supports immune health.
Hydration is also essential, as it can soothe a sore throat and prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate symptoms. Avoiding irritants, such as spicy foods and alcohol, can also aid in recovery.
Understanding the Link Between Allergies and Lingual Tonsil Infections
There is a connection between allergies and lingual tonsil infections. Persistent exposure to allergens can contribute to inflammation and irritation in the throat and tonsillar areas. Allergens can trigger an immune response that leads to inflammation and swelling of the tonsils. While this is not a direct infection, it can create an environment in which the tonsils, including the lingual tonsils, may be more susceptible to infection.
How Allergens Contribute to Tonsilitis
Common allergens that can contribute to tonsillitis include pollen, dust mites, mold, and pet dander. When an allergen is inhaled or ingested, the body’s immune system responds by producing antibodies. These antibodies trigger the release of chemicals, such as histamine, which cause inflammation and swelling. This can result in enlarged tonsils and increased susceptibility to infections.
Taking Charge of Your Health in the Face of Tonsillitis
Managing lingual tonsil infections requires understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, as well as the potential complications if left untreated.
Prevention strategies, such as maintaining good oral hygiene and getting vaccinated, can help reduce the risk of infection. Diet and nutrition can also play a significant role in managing this condition.
Recognizing the link between allergies and tonsillitis can also help in identifying potential triggers and managing symptoms.
If you’re facing recurring tonsillitis or associated symptoms, reach out to us for a consultation. Our team of ENT experts at Penn Medicine Becker ENT and Allergy in New Jersey and Pennsylvania will give you a proper diagnosis and determine what the right course of action is for your situation.

