Tonsillitis is a common health condition that affects many children and can cause concern for parents. Penn Medicine Becker ENT & Allergy offers professionals who specialize in this condition to help young patients overcome the complications that may occur with tonsillitis.
In this article, we aim to provide essential information on tonsillitis, its contagious nature, and how to protect your children from it.
Tonsillitis Snapshot
| What is tonsillitis? | Inflammation of the tonsils, often caused by a viral or bacterial infection. |
| Common symptoms | Sore throat, red/swollen tonsils, fever, difficulty swallowing, bad breath, swollen lymph nodes. |
| Is it contagious? | Yes — especially if caused by viruses or strep bacteria. |
| How it spreads | Through droplets from coughing, sneezing, or close contact. Also by sharing drinks or utensils. |
| Is surgery ever needed? | Sometimes — if tonsillitis is frequent or causes sleep/breathing problems, a tonsillectomy may be considered. |
How Does Tonsillitis Spread?
Tonsillitis is contagious, meaning it can be easily transmitted from one person to another. The infection can spread through direct contact with an infected person’s saliva, nasal secretions, or respiratory droplets produced when they cough or sneeze. It can also be transmitted indirectly by touching contaminated surfaces or objects, such as toys, doorknobs, or utensils, and then touching the mouth or nose.
Children are particularly susceptible to tonsillitis due to their developing immune systems and frequent close contact with other children in settings like schools and daycare centers. It is essential for parents to be aware of the contagious nature of tonsillitis and take necessary precautions to prevent its spread.
What Are the Common Signs of Tonsillitis?
The symptoms of tonsillitis can vary depending on the cause and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include:
- Sore throat
- Swollen and red tonsils
- White or yellow patches on the tonsils
- Difficulty swallowing
- Fever
- Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
- Bad breath
- Headache
- Ear pain
- Fatigue

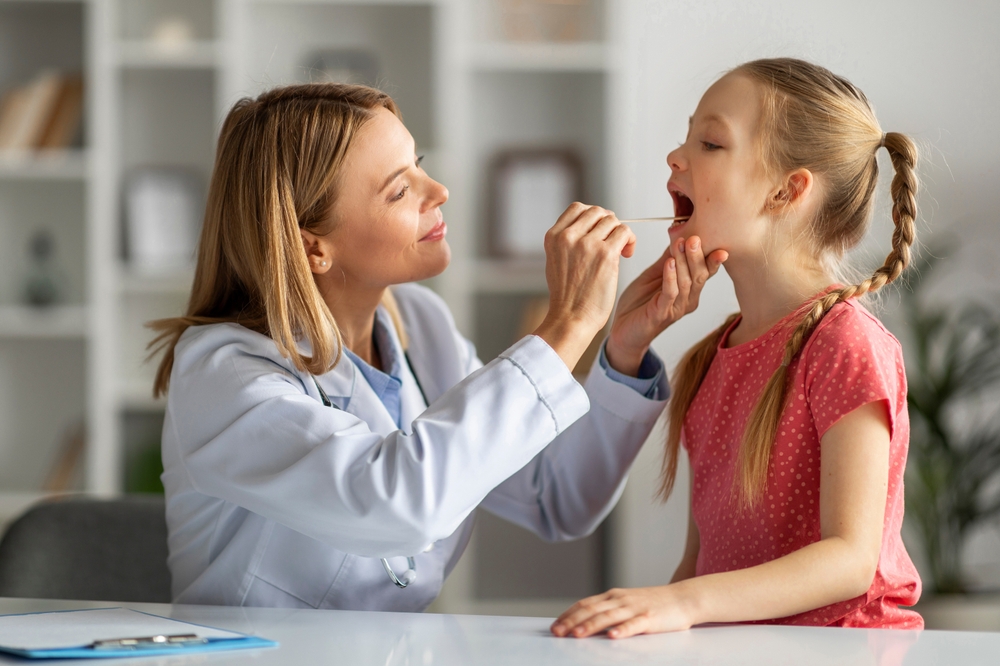
Symptoms of bacterial tonsillitis may be more severe and can include a high fever, severe sore throat, and pus on the tonsils. It is important to monitor your child’s symptoms and consult an ENT specialist if they worsen or do not improve within a few days.
What Causes Tonsillitis?
As mentioned earlier, tonsillitis can be caused by viral or bacterial infections. Viral tonsillitis is more common and can be caused by various viruses, including the common cold, flu, and Epstein-Barr virus (responsible for mononucleosis). Bacterial tonsillitis is most commonly caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, but other bacteria can also be responsible.
In some cases, tonsillitis can be triggered by other factors, such as allergies, irritants like cigarette smoke, or a weakened immune system. Identifying the cause of tonsillitis is crucial for determining the appropriate treatment and preventing complications.
Worried your child’s sore throat might be contagious?
Get answers and the right care from the pediatric ENT team at Penn Medicine Becker ENT & Allergy in New Jersey.
How to Treat Tonsillitis Yourself at Home
The treatment for tonsillitis depends on the cause of the infection, whether it is viral or bacterial. To kill viral tonsillitis bacteria, treatment typically focuses on managing symptoms and providing relief. This may include:

If the tonsillitis is caused by a bacterial infection, a healthcare professional may prescribe antibiotics, such as penicillin or amoxicillin. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished, to ensure the infection is fully treated and prevent complications.
In severe or recurrent cases of tonsillitis, a healthcare professional may recommend a tonsillectomy, which is the surgical removal of the tonsils. This procedure is typically reserved for cases where tonsillitis is causing significant health issues or impacting the child’s quality of life.
Can You Prevent Tonsillitis?
While it may not be possible to completely prevent tonsillitis, there are steps parents can take to reduce the risk of their children developing the infection. These precautions include:
When Should You Call the Doctor About Tonsillitis?

It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional if your child’s tonsillitis symptoms worsen or do not improve within a few days. Additionally, seek medical attention if your child experiences any of the following:
Prompt medical attention can help ensure your child receives the appropriate treatment and prevent potential complications associated with tonsillitis.
Are There Complications Associated with Tonsillitis?
While most cases of tonsillitis resolve without complications, there are instances where untreated or severe tonsillitis can lead to more serious health issues. Some potential complications associated with tonsillitis include:
Peritonsillar abscess
A collection of pus that forms near the tonsils, causing severe pain and difficulty swallowing. This condition requires prompt medical attention and treatment, which may include antibiotics or drainage of the abscess.
Middle ear infection (otitis media)
In some cases, the infection causing tonsillitis can spread to the middle ear, leading to pain, fever, and hearing difficulties.
Rheumatic fever
Although rare, untreated strep throat (a bacterial cause of tonsillitis) can lead to rheumatic fever, a condition that affects the heart, joints, and nervous system.
Obstructive sleep apnea
Chronic or recurrent tonsillitis can cause the tonsils to become enlarged, obstructing the airway during sleep and leading to sleep apnea, a condition characterized by pauses in breathing during sleep.
It is essential to seek medical attention for tonsillitis to minimize the risk of these complications and ensure appropriate treatment.
How Long Does it Take to Recover from Tonsillitis?
The recovery time for tonsillitis depends on the severity of the infection and the individual’s overall health. In most cases, symptoms of viral tonsillitis begin to improve within a few days and resolve completely within one to two weeks. For bacterial tonsillitis treated with antibiotics, symptoms usually start to improve within 24 to 48 hours of starting the medication.
It is essential to follow the healthcare professional’s advice and complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished, to ensure the infection is fully treated and prevent the risk of complications.
What is the Prognosis for People with Tonsillitis?
The outlook for both children and adults with tonsillitis is usually very good. Most people recover fully without any lasting issues. However, some individuals may develop recurrent tonsillitis, which can significantly impact their quality of life and may require additional medical interventions, such as a tonsillectomy.
Maintaining good hygiene practices, staying up-to-date on vaccinations, and seeking prompt medical attention for tonsillitis symptoms can help improve the prognosis and minimize the risk of complications.

